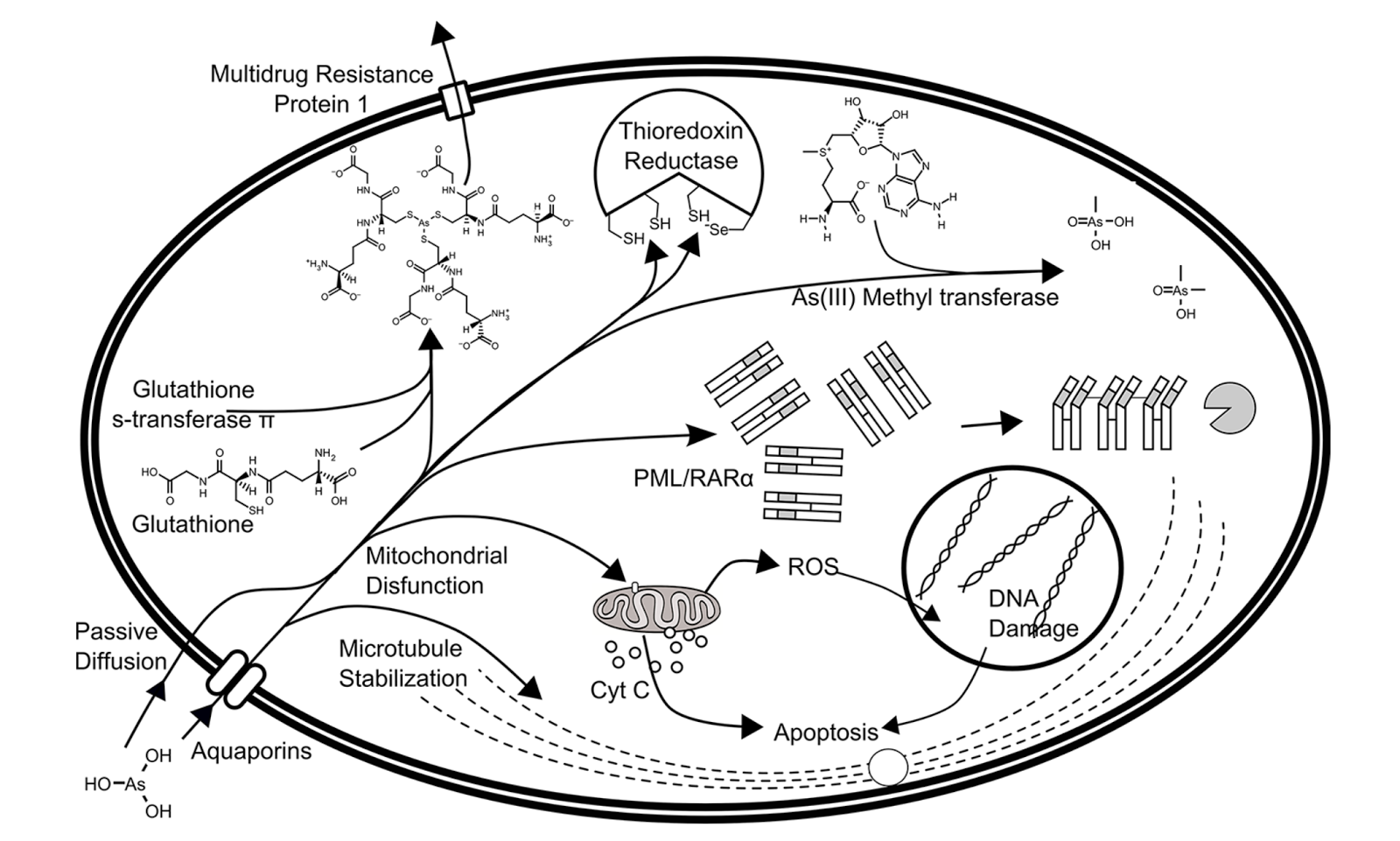
Figure 1. Toxicity of arsenous acid in the human cell. Arsenic trioxide (As2O3) is converted to arsenous acid at physiological pH. Upon entering cells via passive diffusion or via aquaporins, arsenous acid causes oxidative stress, can interfere with phosphorylation reactions, and can disrupt microtubule polymerization/depolymerization. Image from Swindell et al. (2013)
hzv_arsenic_Screen Shot 2017-03-09 at 12.45.27 AM
April 3, 2017 | 0 comments